MQTT Source
The DSK Edge Agent service supports integration of external data sources using the MQTT messaging protocol.
Your MQTT client needs to connect to our MQTT message broker (eclipse-mosquitto) and publish MQTT messages with a specific payload format on one of our pre-defined MQTT topics or using the custom/configurable MQTT topics. The published message will be processed from our main DSK Edge Agent service (dsk-agent) and enriched to achieve data authenticity and integrity support.
Such an MQTT client could be any of your existing edge services or implemented specifically for the use case in your desired programming language and run as additional Docker sidecar container.
We recommend the configuration of the MQTT source based on twins which can be done with our Agent Companion and is described in the subsequent chapters.
Connect to the MQTT broker
By default the MQTT broker is only available within the Docker bridge network edge-net with the service name mosquitto-server on port 1883.
Accordingly you need to either connect your custom MQTT client running as Docker container to the edge-net
or publish/expose the port of the MQTT broker on the host with a configuration like the following:
# MQTT broker/server
mosquitto-server:
image: eclipse-mosquitto:1.6
networks:
- edge-net
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:1883:1883" # publish/expose port to host
which enable access on localhost with port 1883.
In the default setup we do not use user/password authentication nor SSL/TLS since we are in a closed environment. If you want to refine this setup please talk to your contact person at Tributech or send an email to our Customer Advisory Team.
For testing purposes we can recommend tools like MQTTX or MQTT Explorer.
If the port was published to the host as described above we can connect with such tools and post test messages (as used in the subsequent samples).
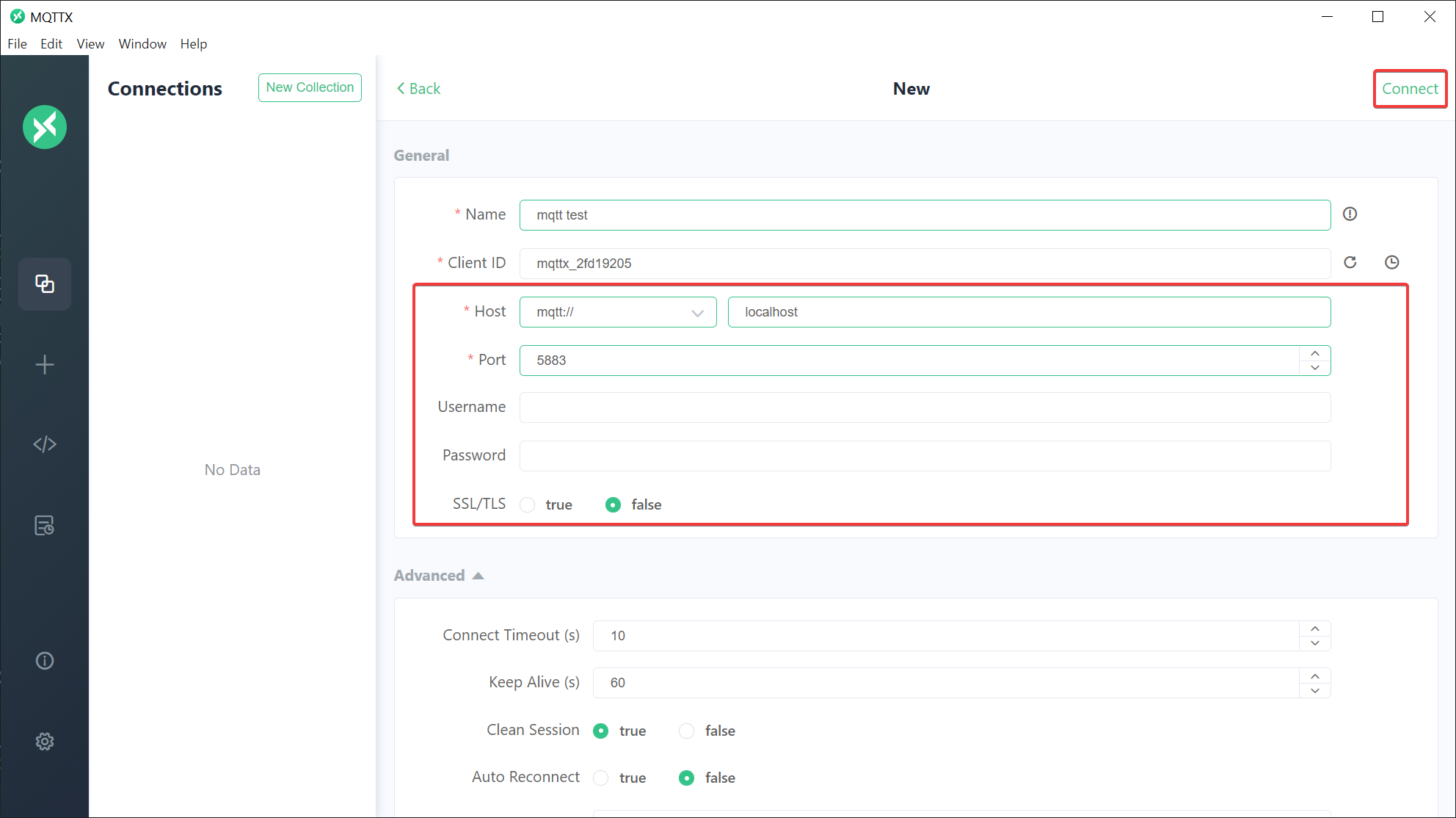 Register for the wildcard topic
Register for the wildcard topic # to see all messages.
If you are connecting to your agent via SSH and are using SSH tunneling/port-forwarding you might want to additionally forward traffic for the MQTT broker port 1883 for testing purposes so that you can connect from your local machine.
ssh <vm-user>@<vm-ip> -L 5000:localhost:5000 -L 1883:localhost:1883
# e.g.
ssh tributech@20.86.158.183 -L 5000:localhost:5000 -L 1883:localhost:1883
Otherwise you need to ensure that the port 1883 is accessible on the edge device (firewall rules).
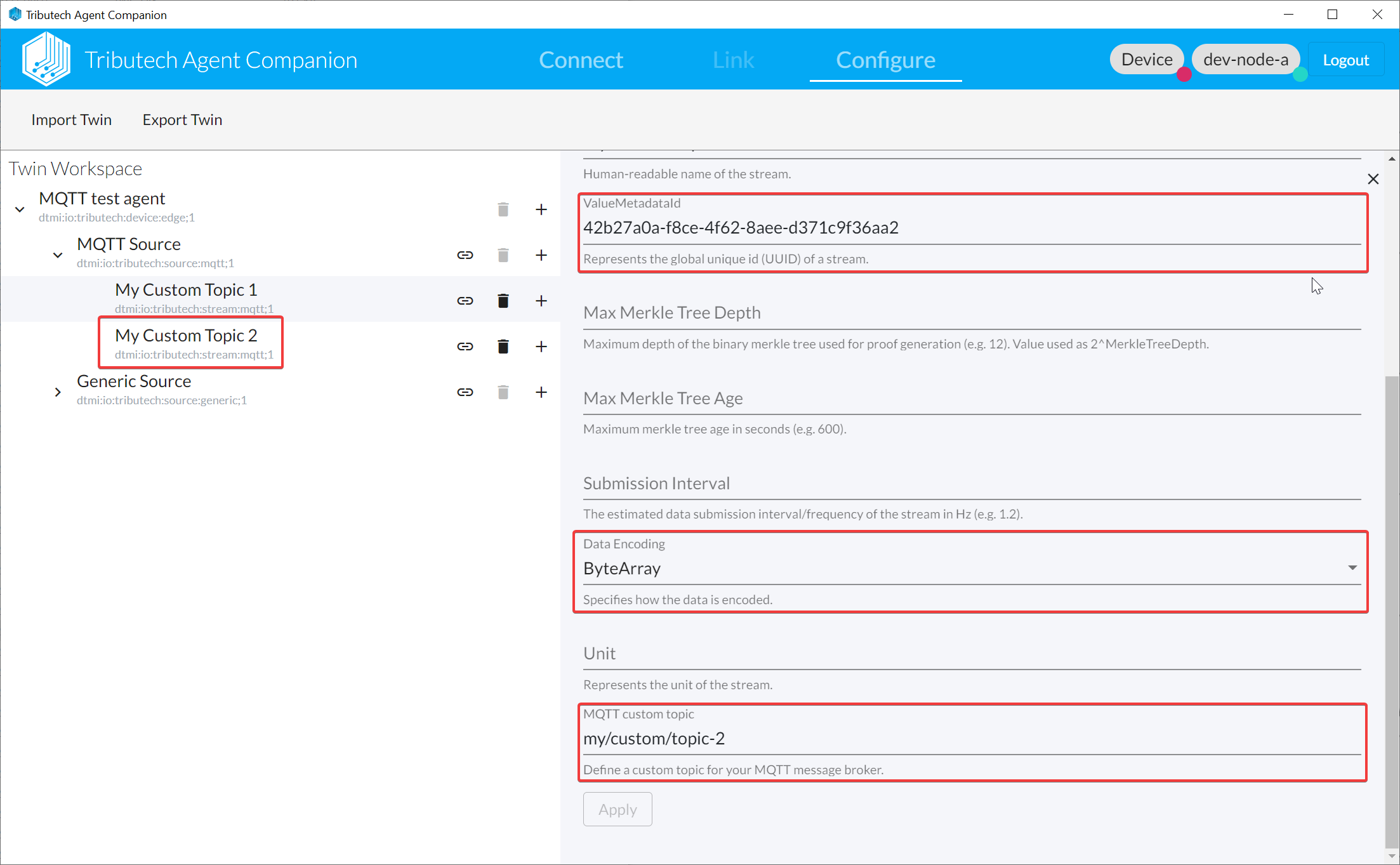
Custom/Configurable MQTT topics
You can configure a custom MQTT topic for a stream on which the main DSK Edge Agent service will listen and process all MQTT messages published at the MQTT broker.
The mapping of MQTT message to the value for the stream works like the following:
ValueMetadataId: All MQTT messages matching the MQTT custom topic will be created as value with ValueMetadataID of the stream.Timestamp: Current time of the edge-device when the topic gets read by the DSK Edge Agent.Values: The payload in raw-bytes representing the value (see Data encoding).
Configure:
- Open the Agent Companion, login to the DSK Node and connect with the DKS Edge Agent
- Add MQTT Source
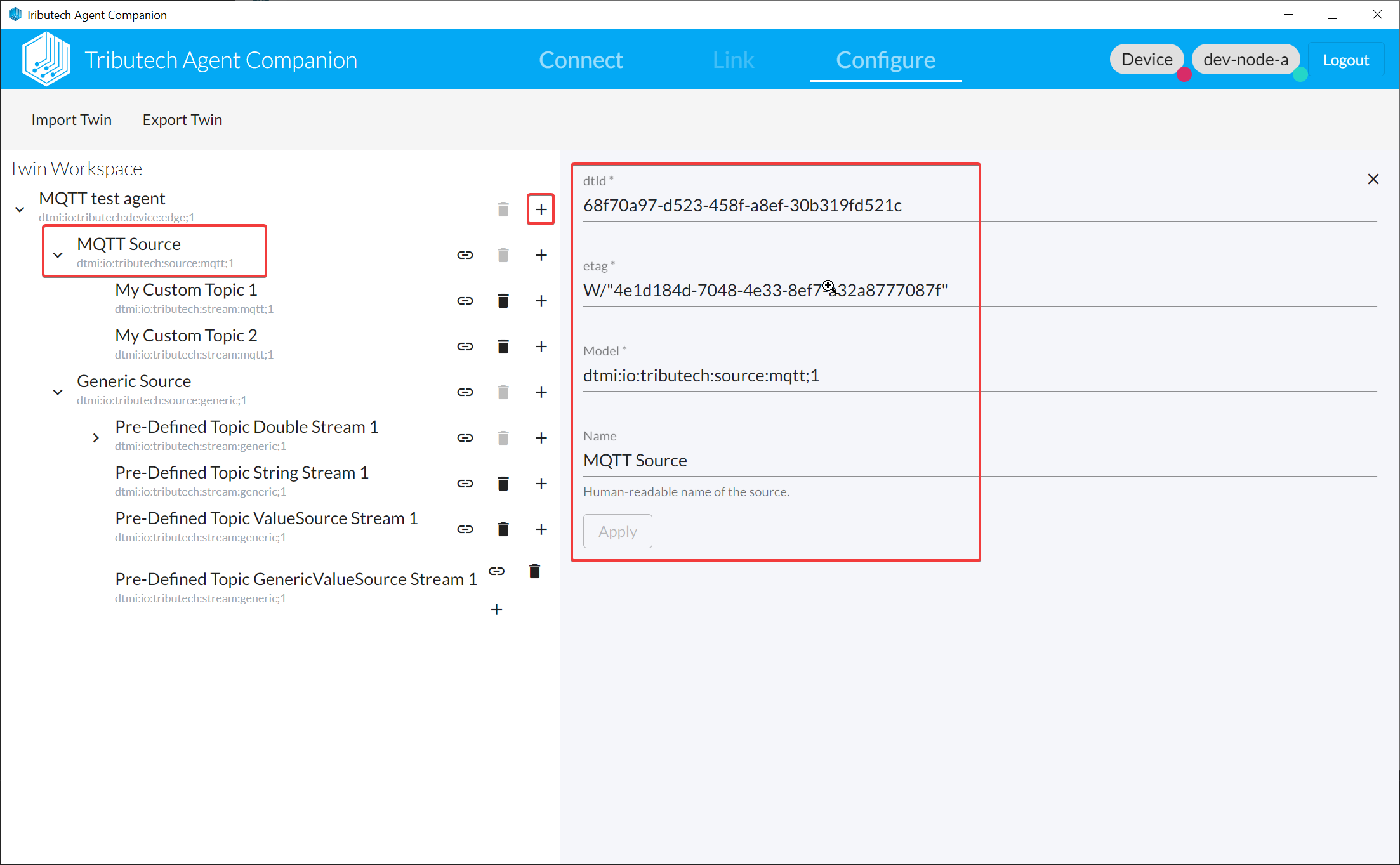
- Add MQTT Stream(s)
MQTT custom topic must follow the MQTT specification and the same topic can not be used for multiple streams.
Data Encoding defines the actual value type (since provided as raw-bytes in the message).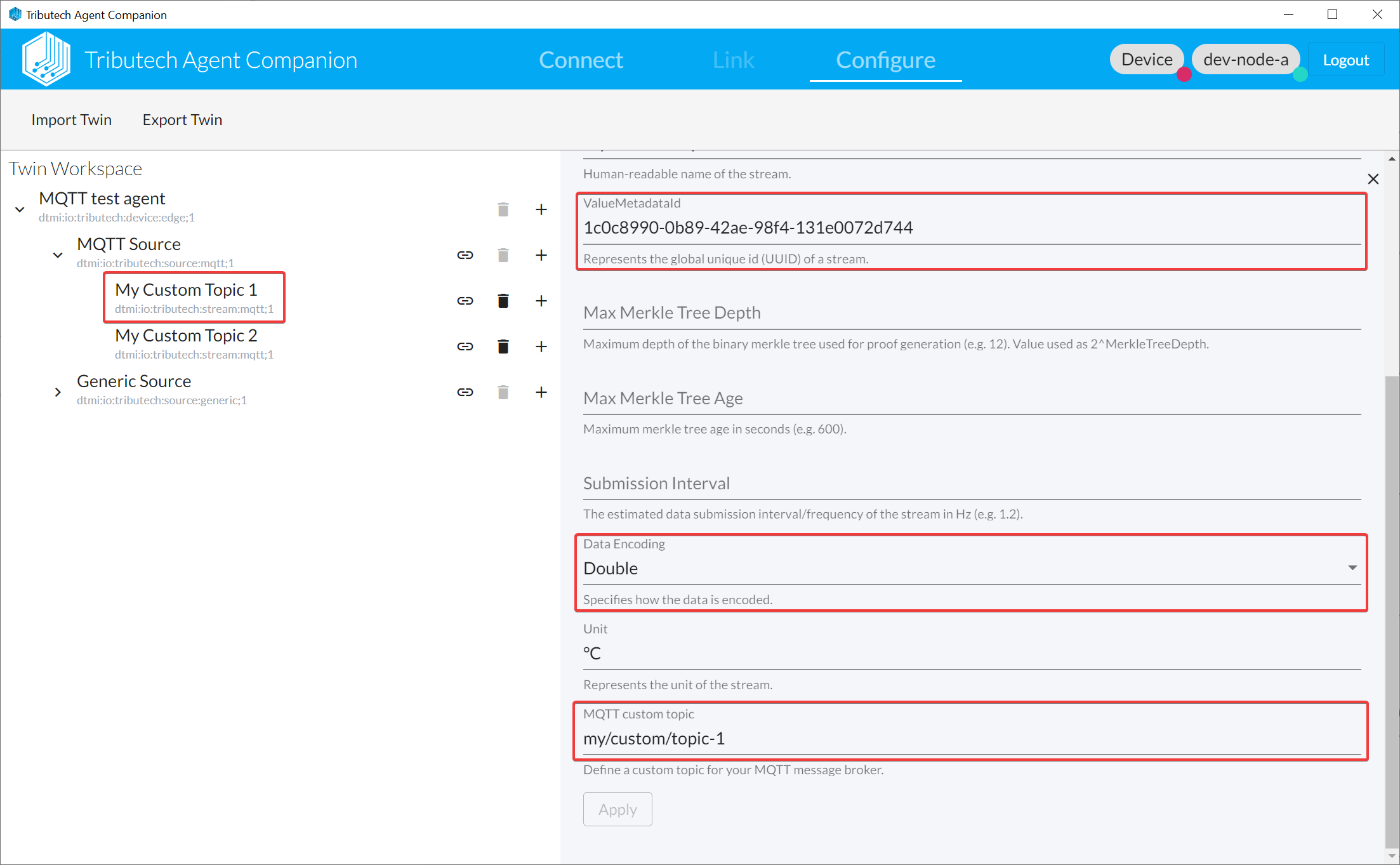
- Upload To Device
Test and verify:
- Publish MQTT message for configured topic
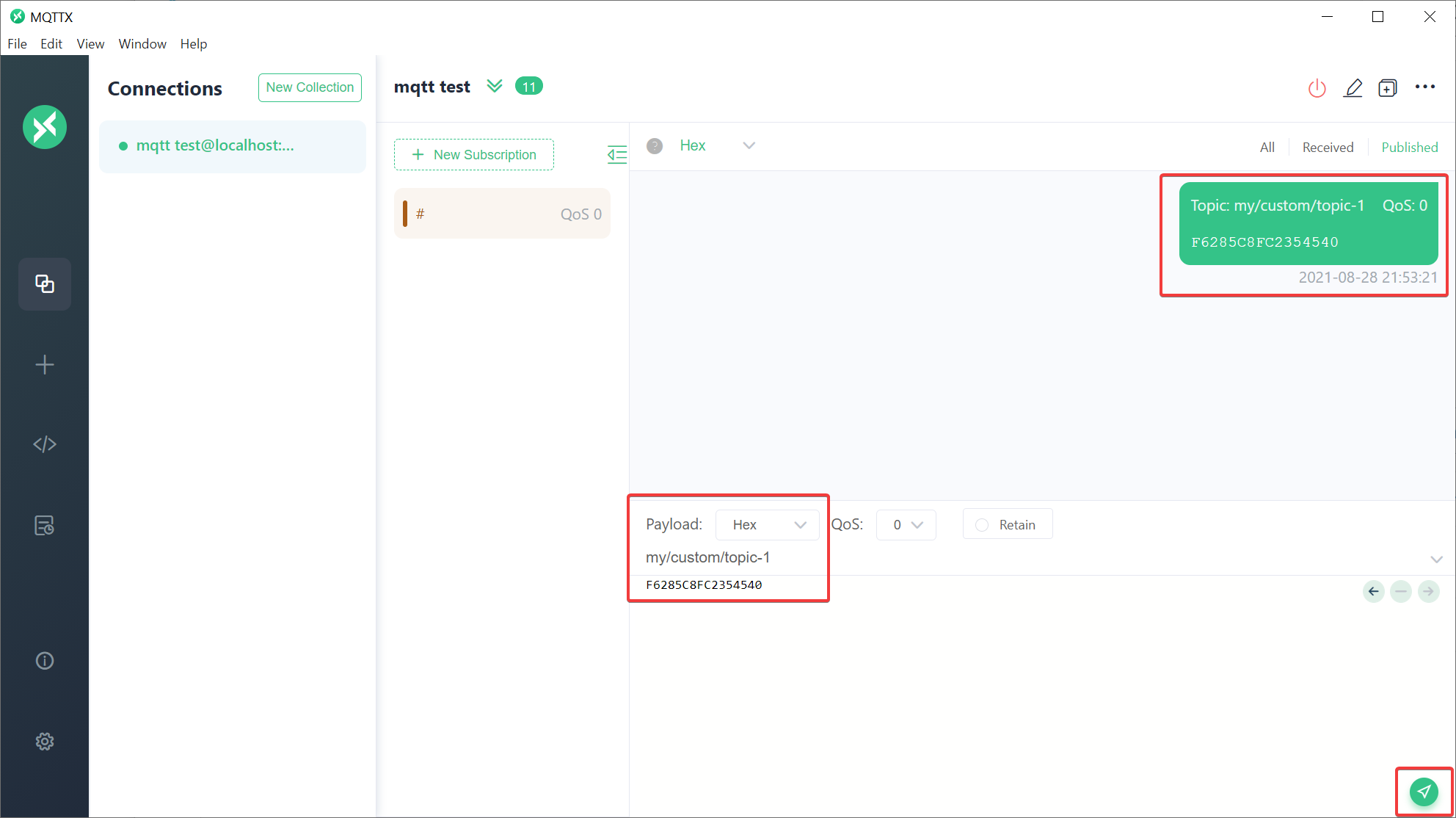
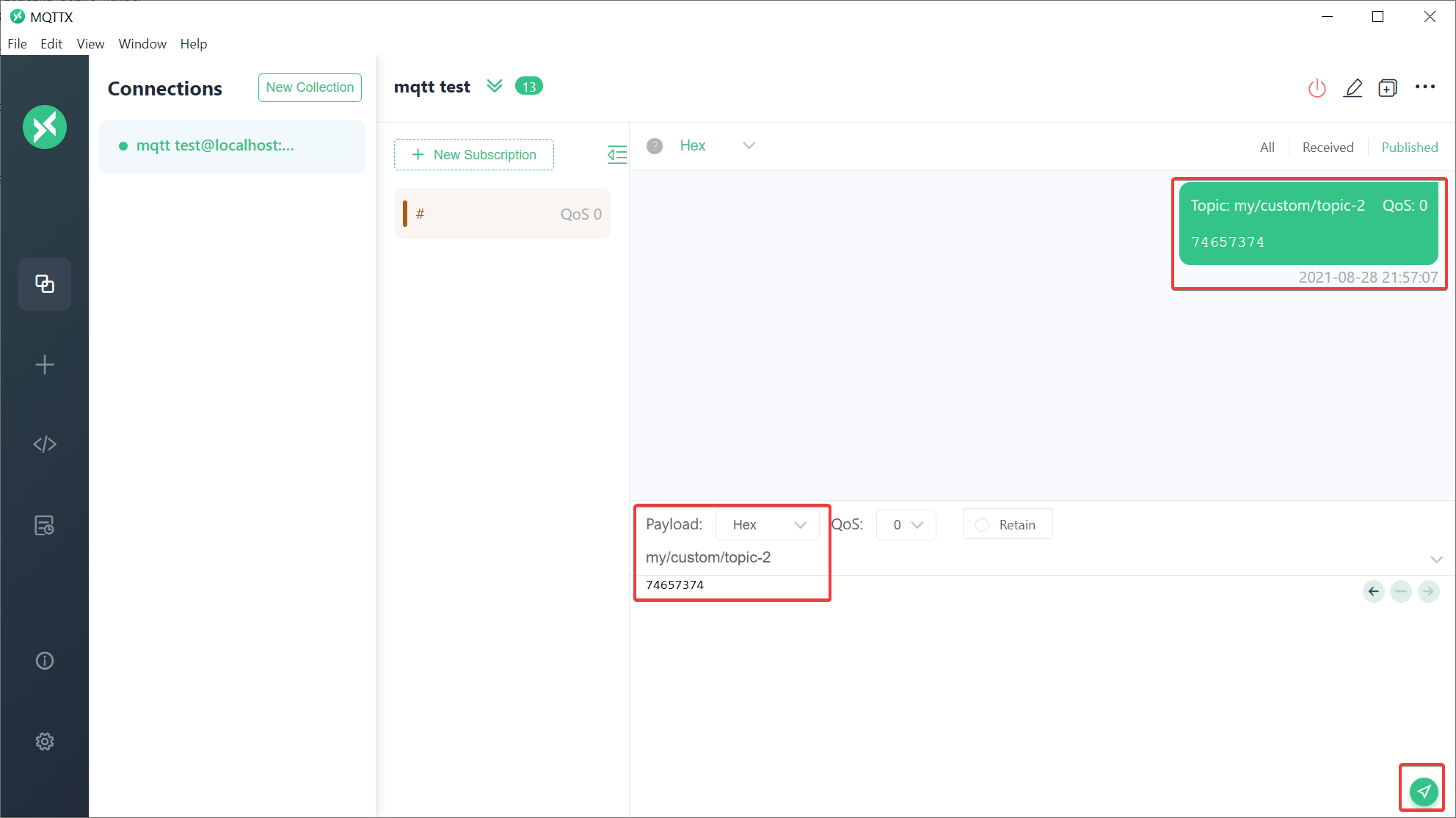
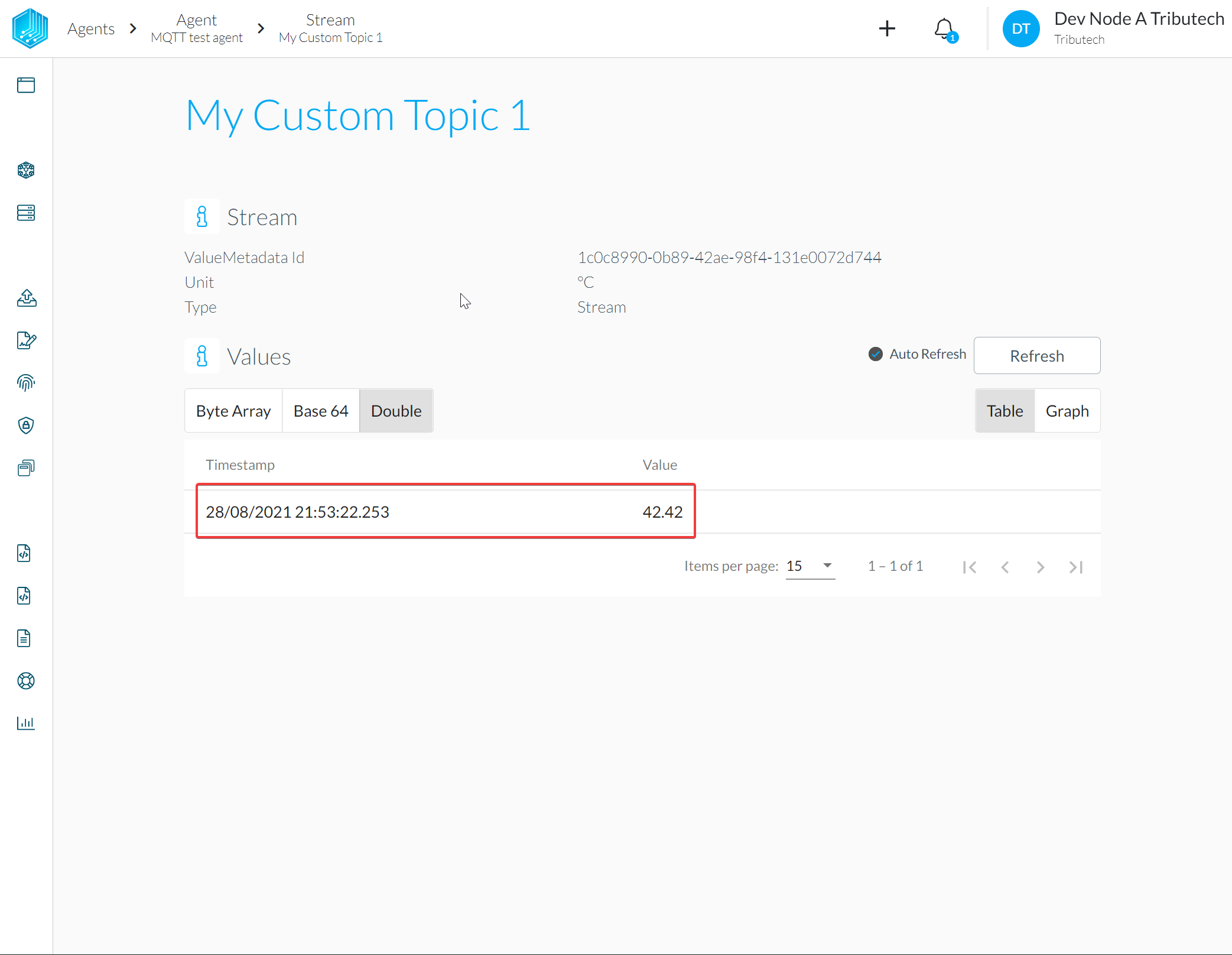
- Verify value for published message in DataSpace-Admin at Streams of Agent
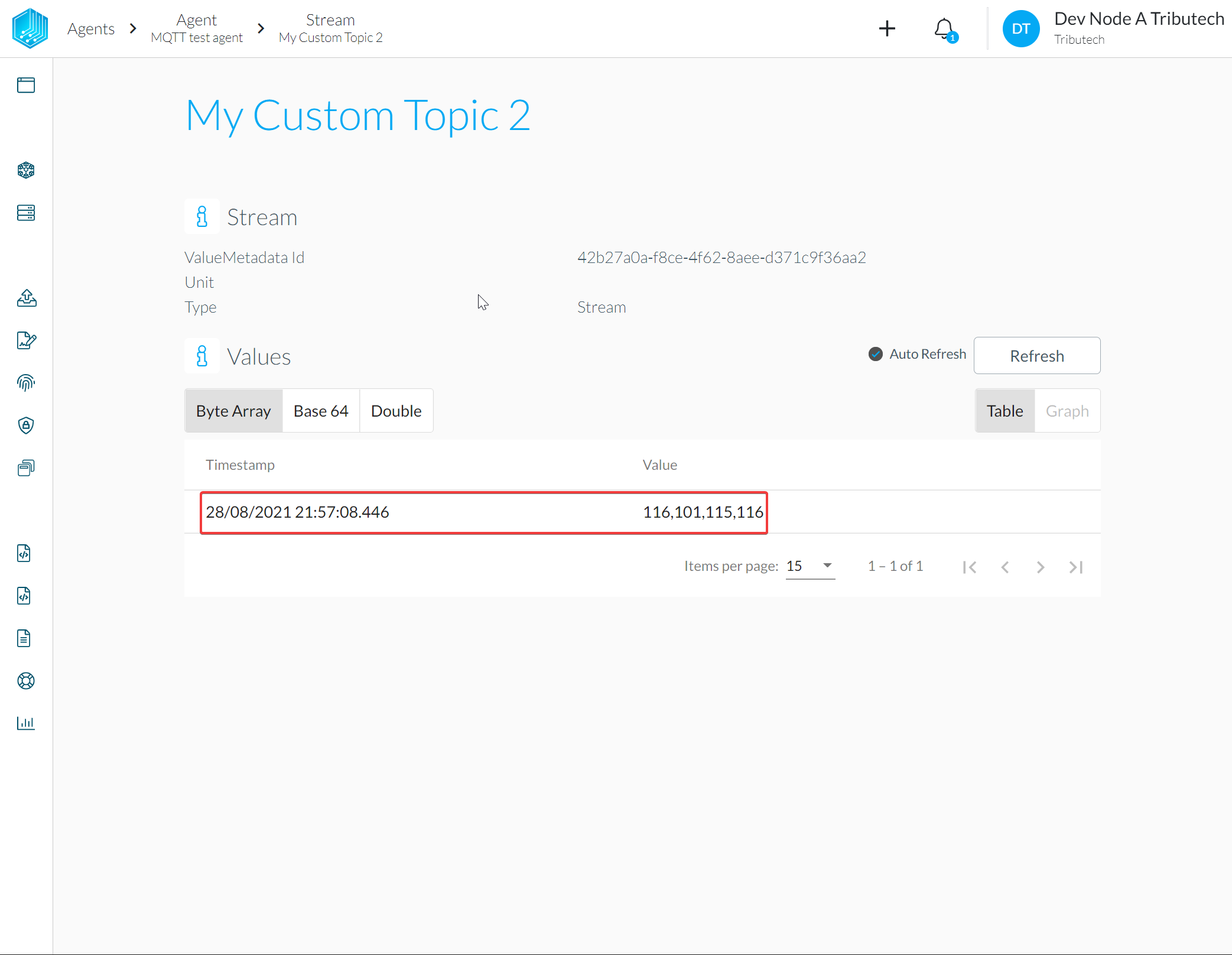
Predefined MQTT topics
The DSK Edge Agent has certain predefined MQTT topics he is listening on. If we publish MQTT messages in the required format on such topics they are automatically processed and converted into values for streams.
For representation as twins in the configuration we use Generic Source and Generic Stream.
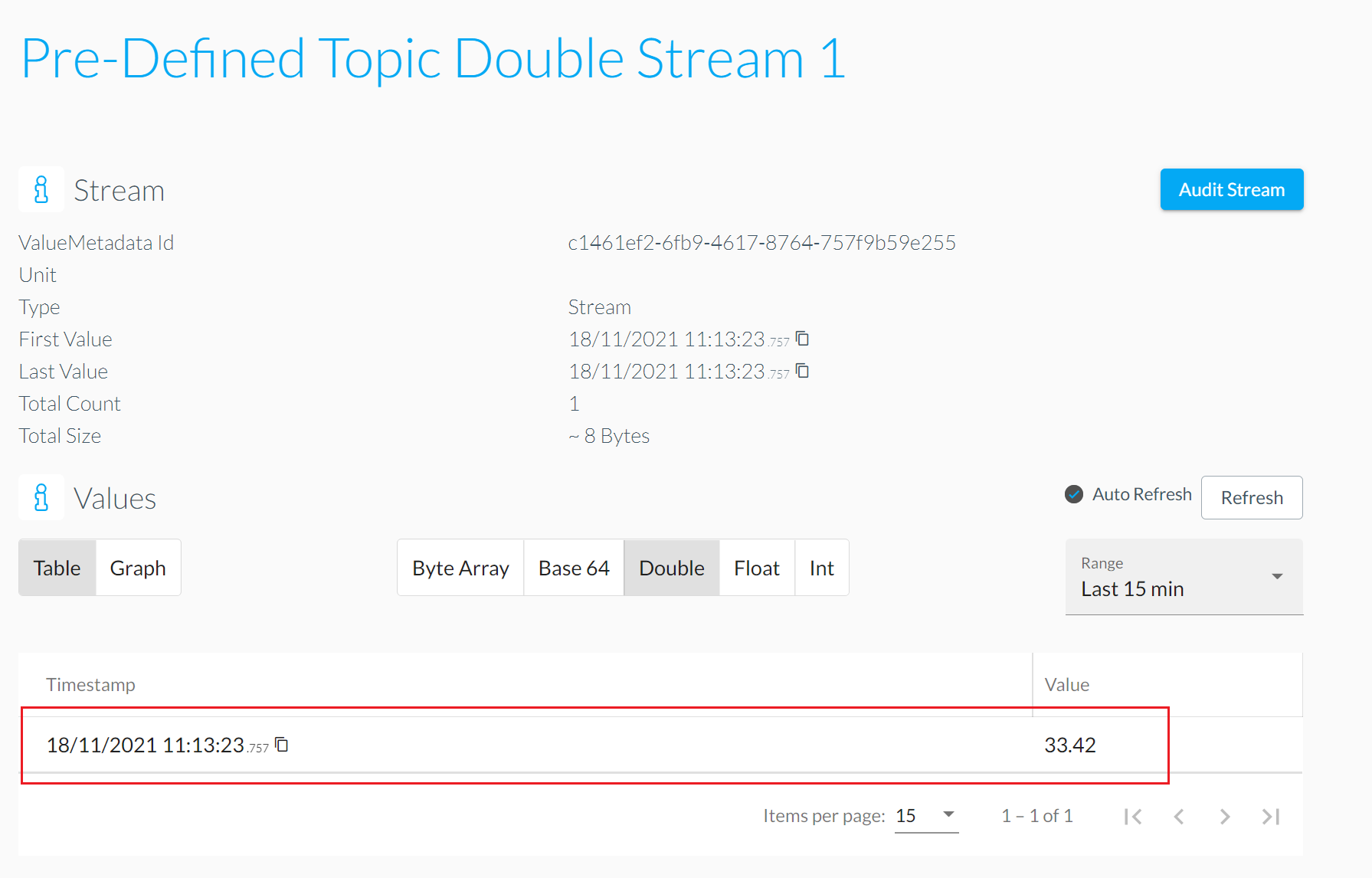
Double topic
TOPIC: DSK/EdgeAgent/Double/<ValueMetadataId>
For publishing of floating point number values represented as double.
The mapping of MQTT message to the value for the stream works like the following:
ValueMetadataId: Taken fromValueMetadataIdplaceholder inside the topic.Timestamp: Current time of the edge-device when the topic gets read by the DSK Edge Agent.Values: The payload in raw-bytes of an little-endian-encoded 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point number (see Data encoding).
Configure:
- Open the Agent Companion, login to the DSK Node and connect with the DKS Edge Agent
- Add Generic Source
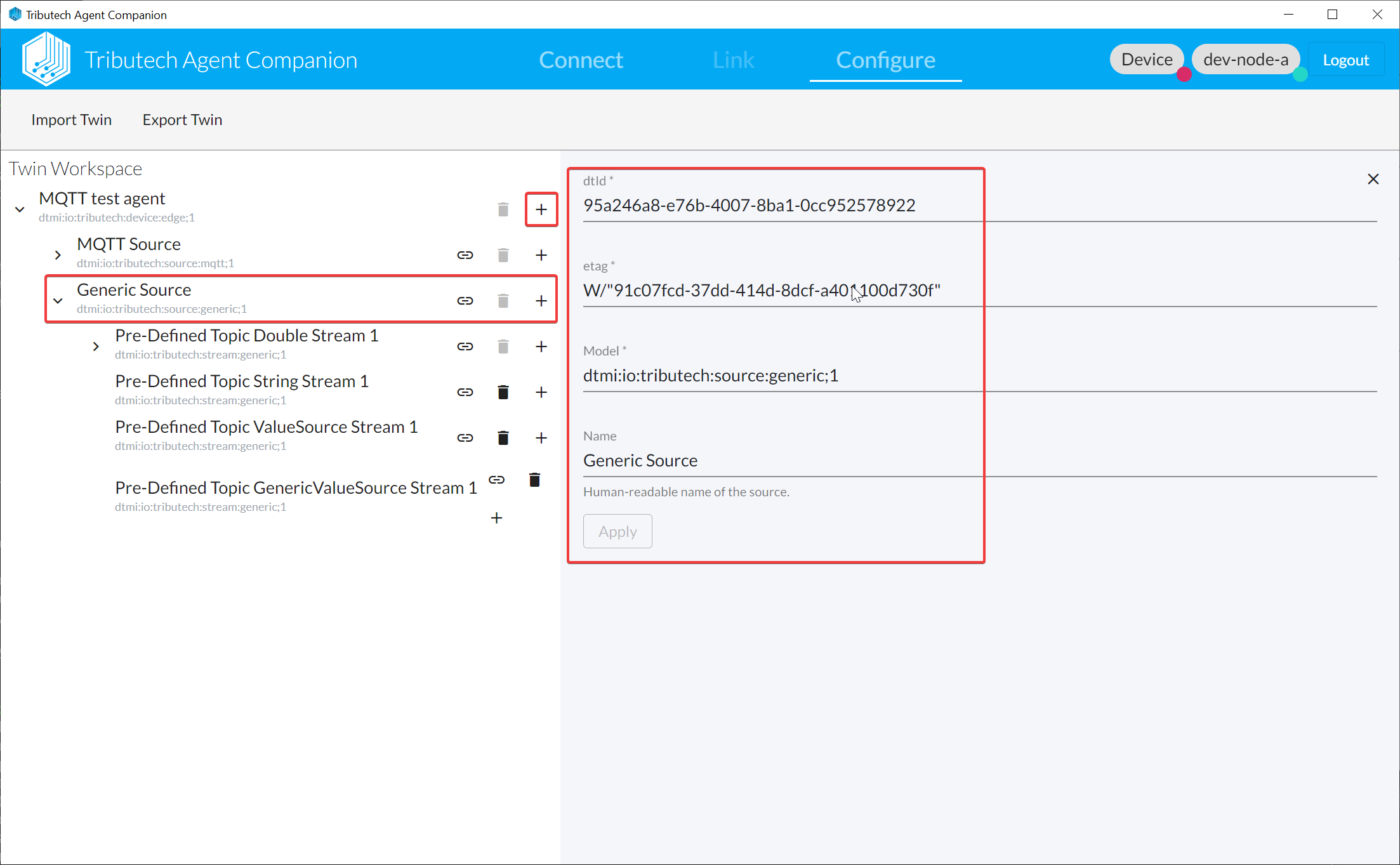
- Add Generic Stream(s) and use
ValueMetadataIdthat will be used in the topic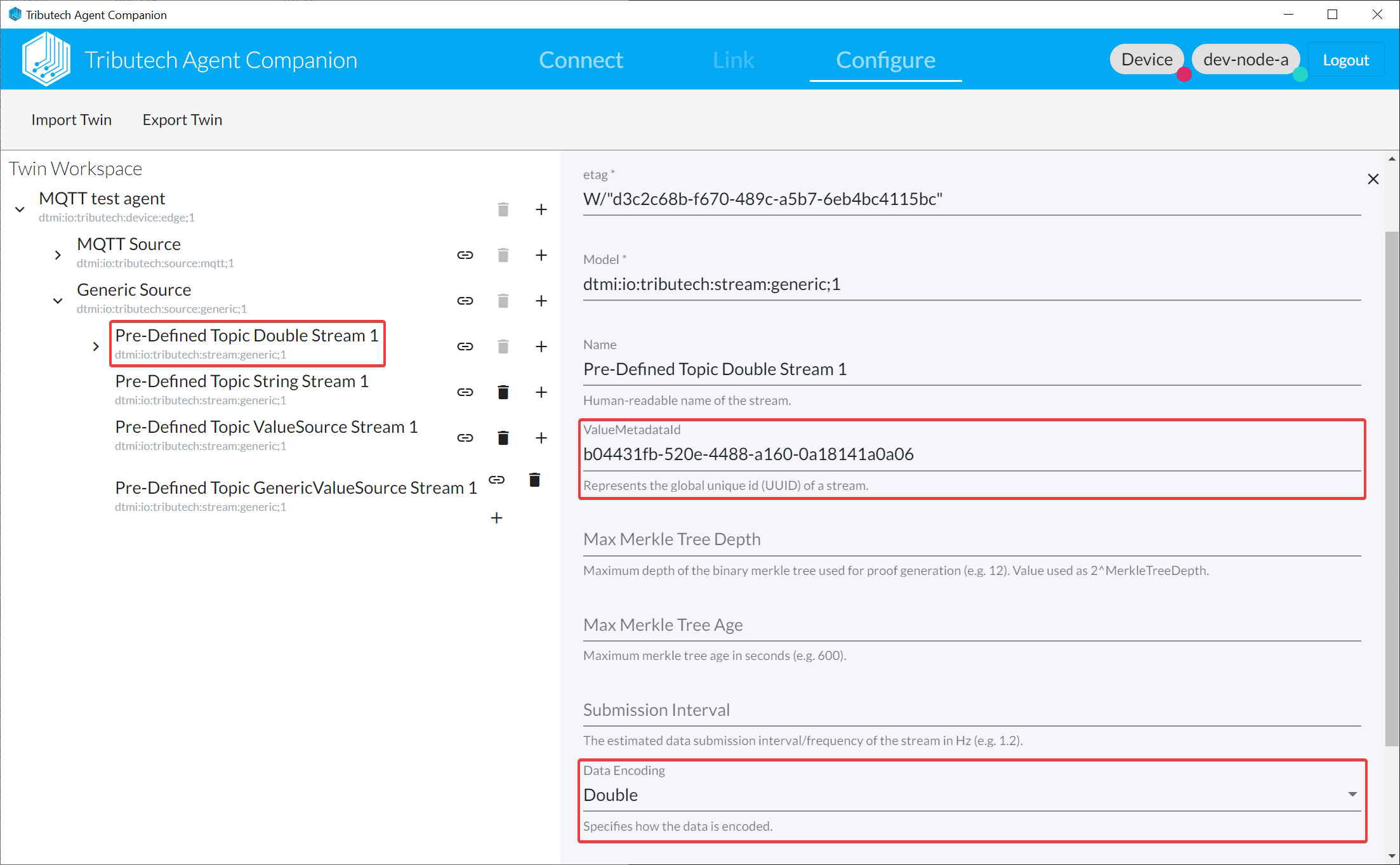
- Upload To Device
Test and verify (sample uses different id's):
- Publish MQTT message for double topic with
ValueMetadataId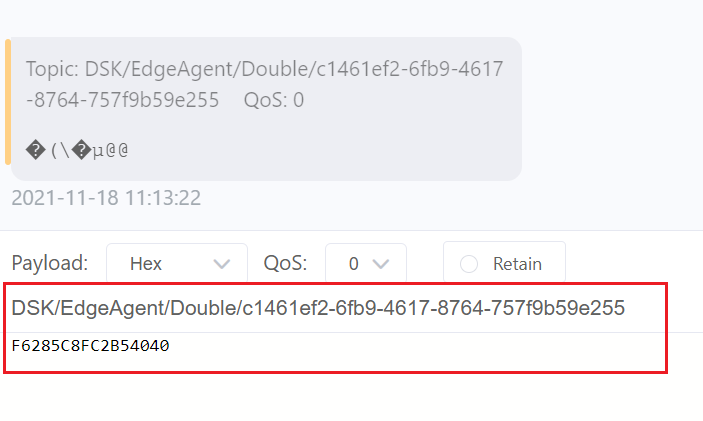
- Verify value for published message in DataSpace-Admin at Streams of Agent
String topic
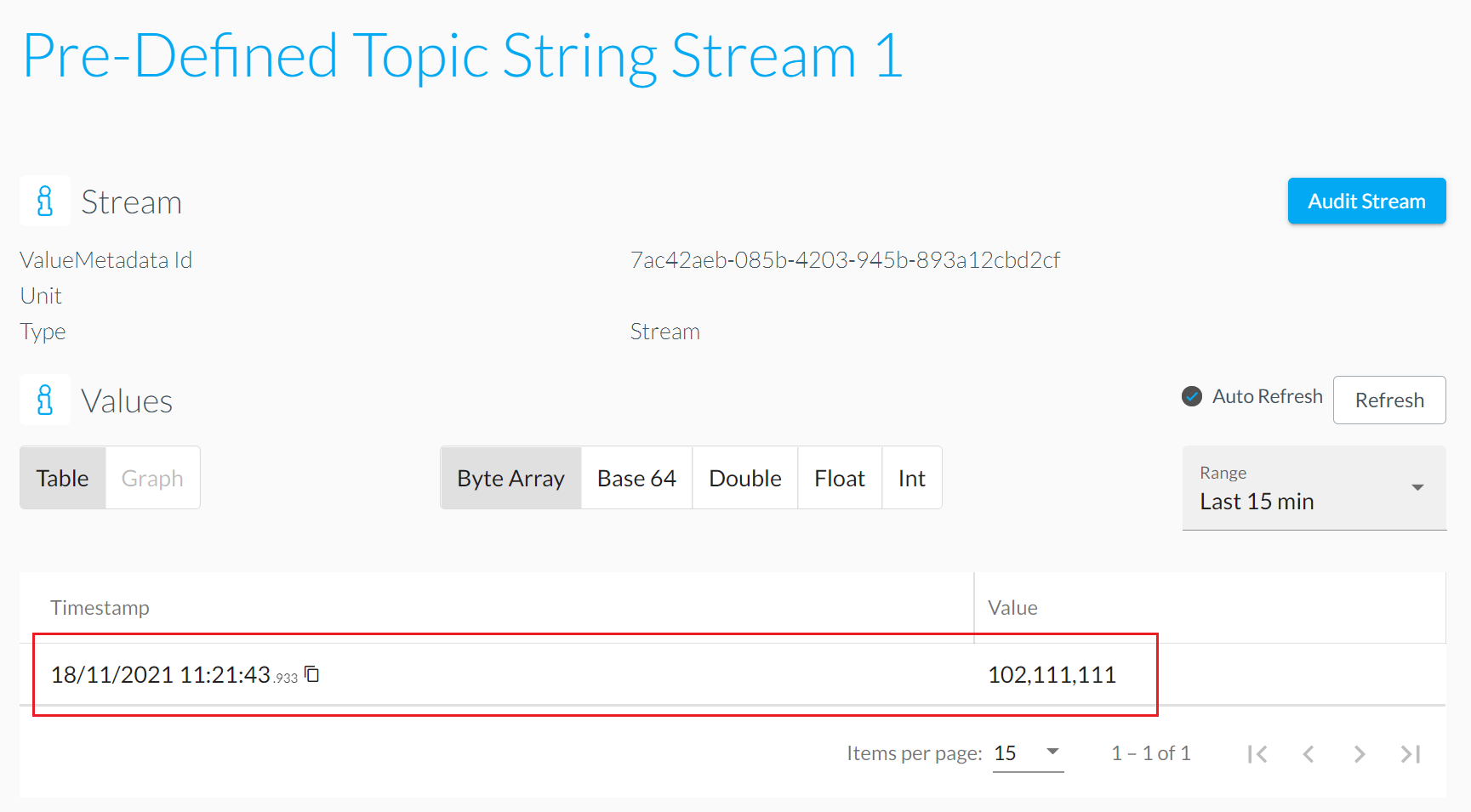
TOPIC: DSK/EdgeAgent/String/<ValueMetadataId>
For publishing of UTF-8 encoded strings.
The mapping of MQTT message to the value for the stream works like the following:
ValueMetadataId: Taken fromValueMetadataIdplaceholder inside the topic.Timestamp: Current time of the edge-device when the topic gets read by the DSK Edge Agent.Values: The payload in raw-bytes of an UTF8-encoded string (see Data encoding).
Configure:
- Open the Agent Companion, login to the DSK Node and connect with the DKS Edge Agent
- Add Generic Source

- Add Generic Stream(s) and use
ValueMetadataIdthat will be used in the topic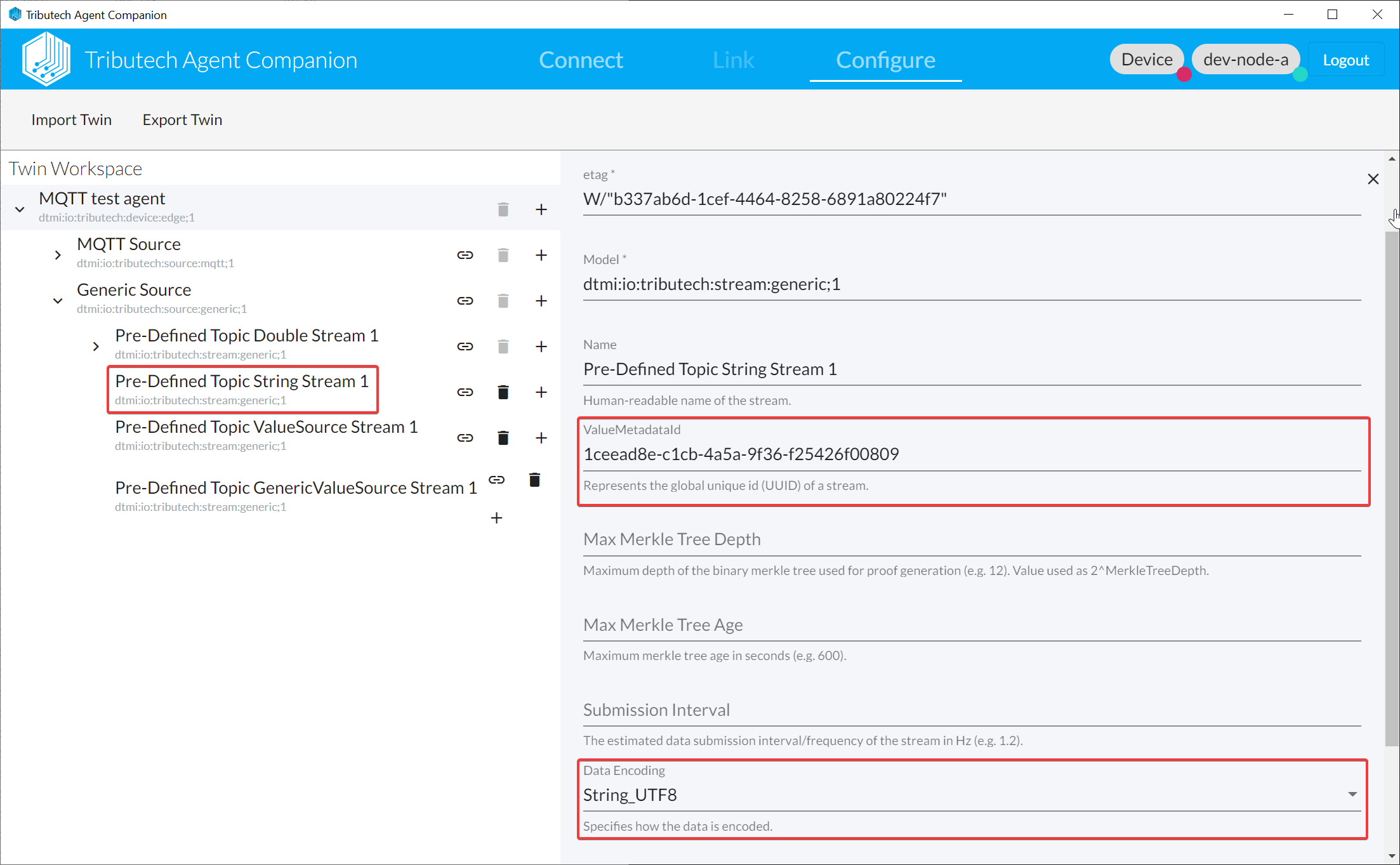
- Upload To Device
Test and verify (sample uses different id's):
- Publish MQTT message for string topic with
ValueMetadataId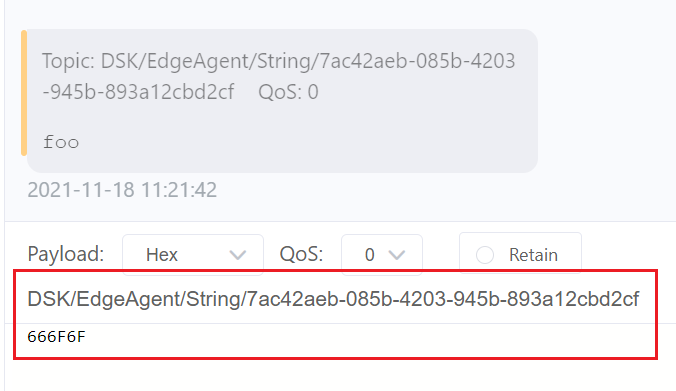
- Verify value for published message in DataSpace-Admin at Streams of Agent
ValueSource topic
TOPIC: DSK/EdgeAgent/ValueSource
For publishing of various typed values with custom timestamp and ValueMetadataId (UUID).
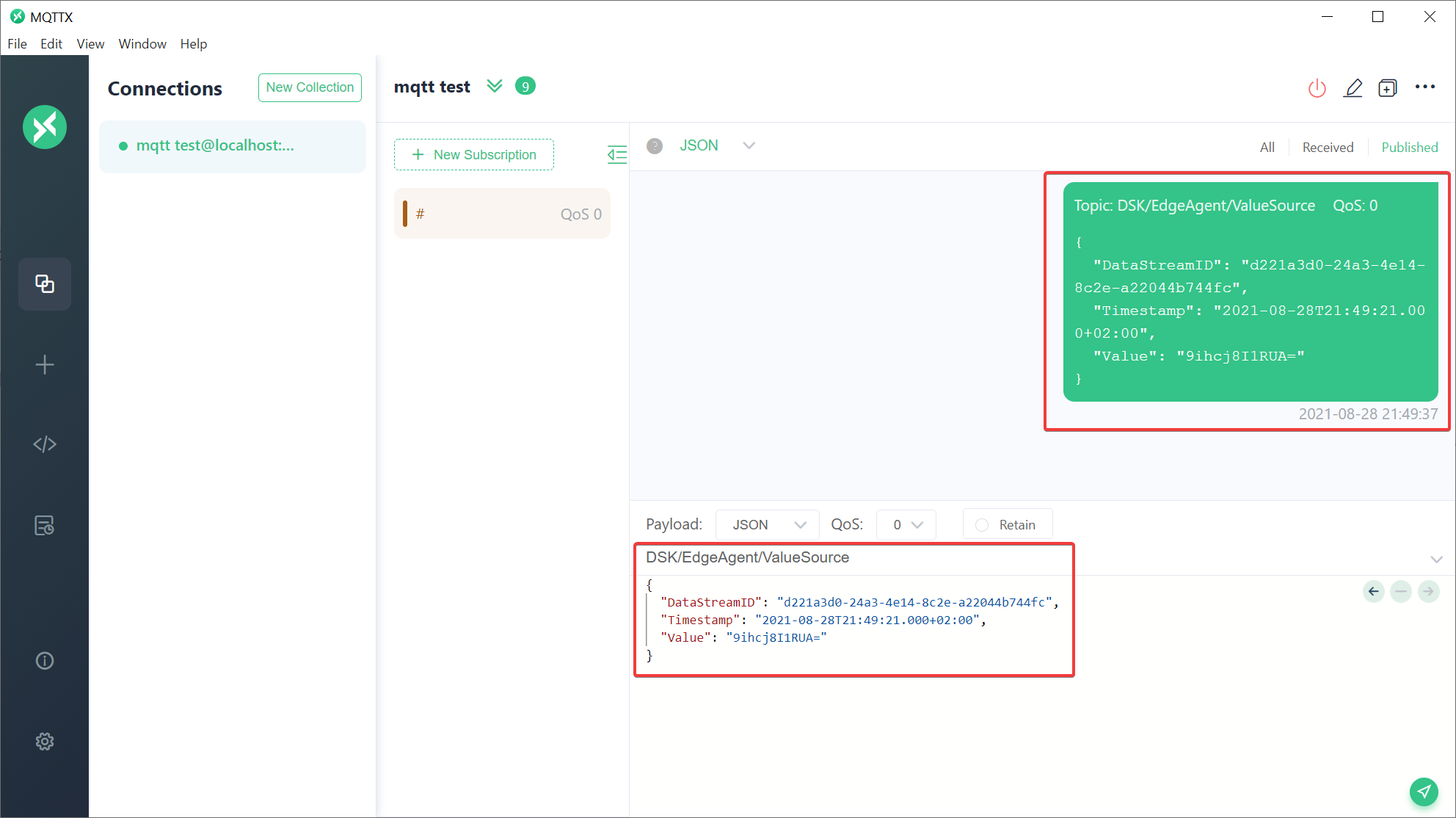
The payload provided for the topic needs to be a UTF8-encoded string which represents a JSON-object as shown in the following example:
{
"DataStreamID": "8235326b-6f43-4402-8bdf-bcfbd0999b70", // ValueMetadataId of the stream
"Timestamp": "2020-01-01T00:00:01+00:00", // Timestamp for the value
"Value": "9ihcj8I1RUA=" // Base64-encoded raw-bytes of the actual value
}
The mapping of MQTT message to the value for the stream works like the following:
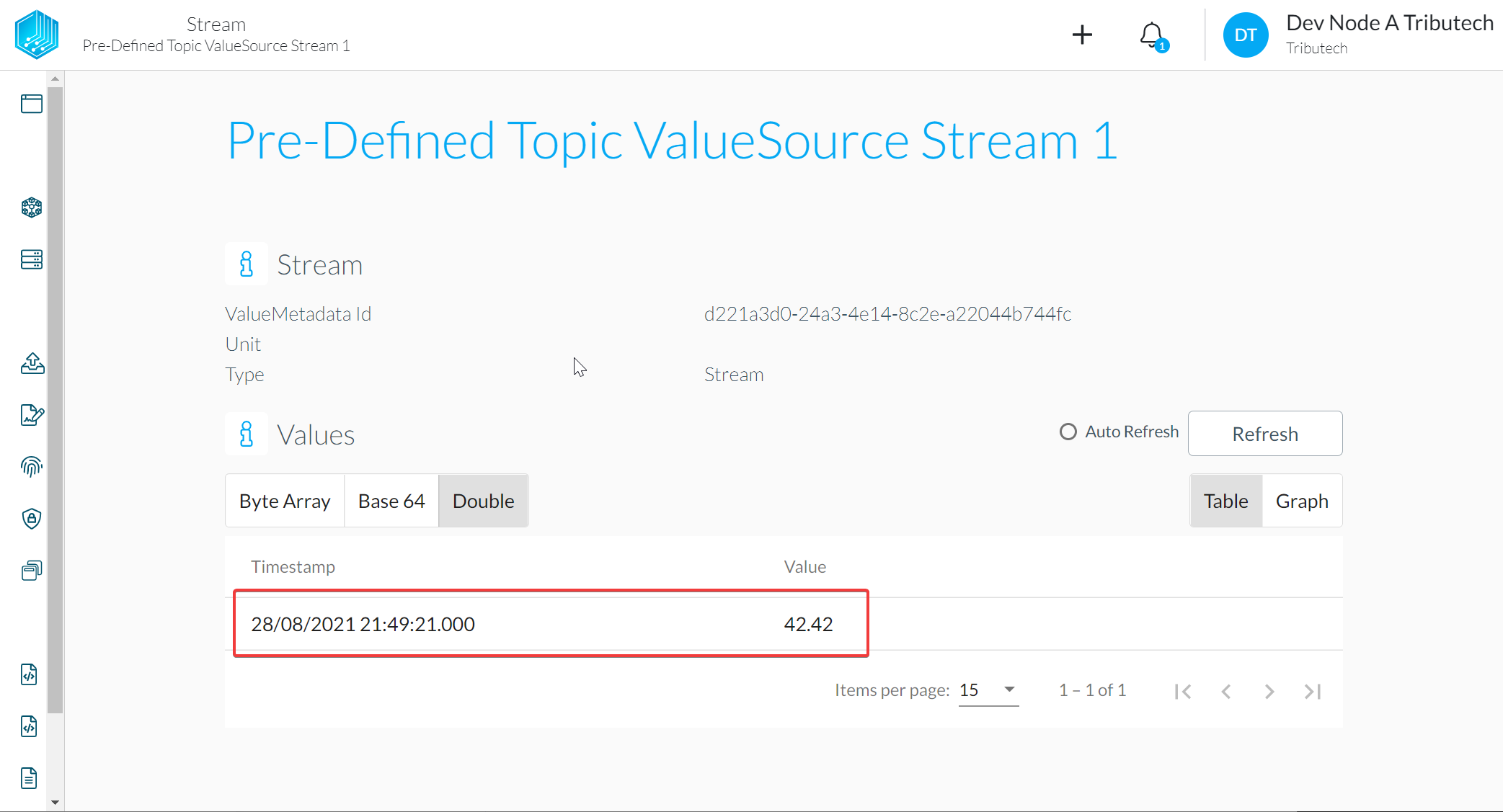
ValueMetadataId:DataStreamIDfrom the JSON-object. Currently there is no check that a matching stream exist we however recommend to create a Generic Stream for each publishedDataStreamIDfor easier management.Timestamp:Timestampfrom the JSON-object. (Format ISO 8601-1:2019)Values:Valuefrom the JSON-object as Base64-encoded raw-bytes of the actual value (see Data encoding).
Configure:
- Open the Agent Companion, login to the DSK Node and connect with the DKS Edge Agent
- Add Generic Source

- Add Generic Stream(s) with
ValueMetadataIdmatching theDataStreamIDin the message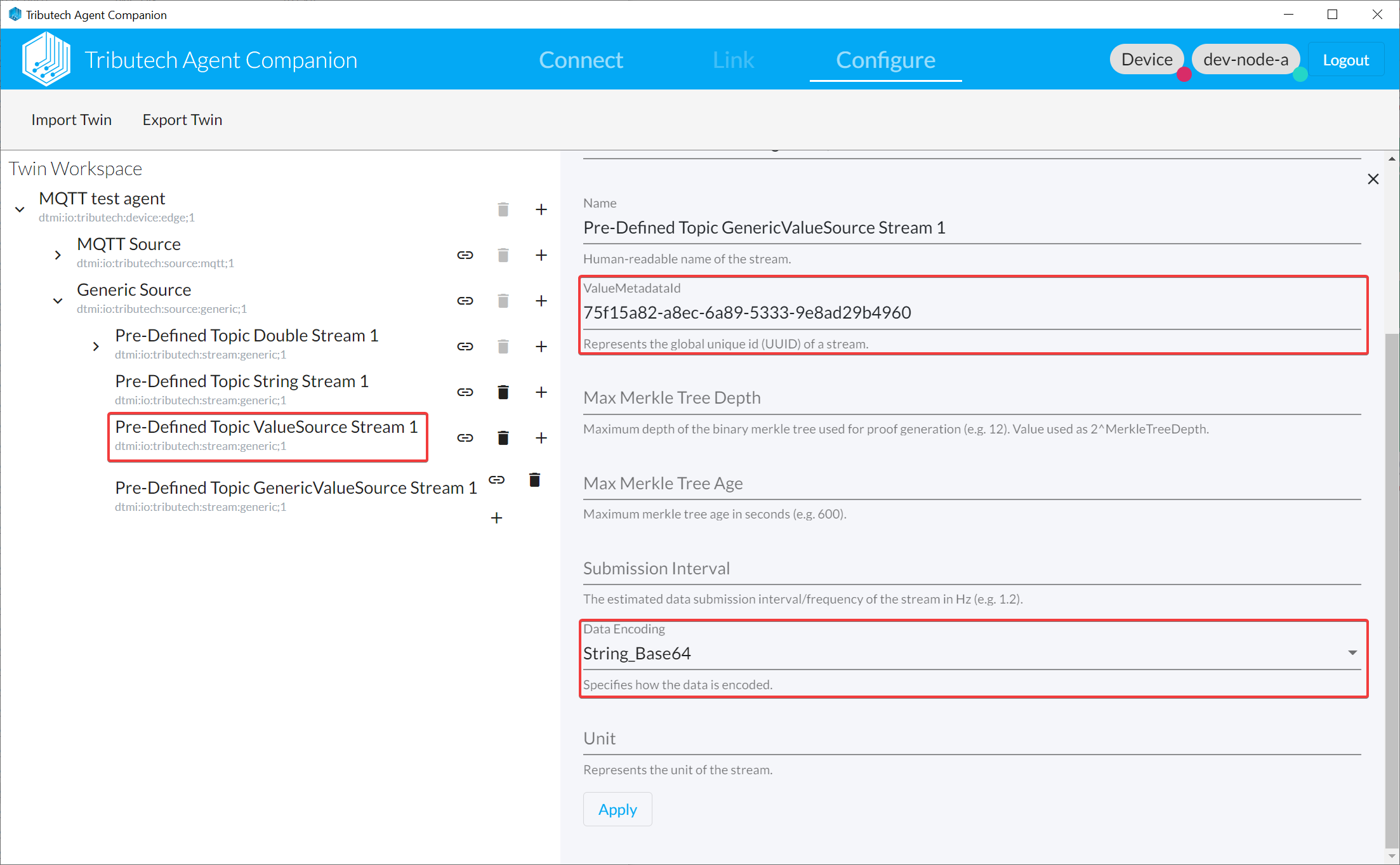
- Upload To Device
Test and verify:
- Publish MQTT message on topic
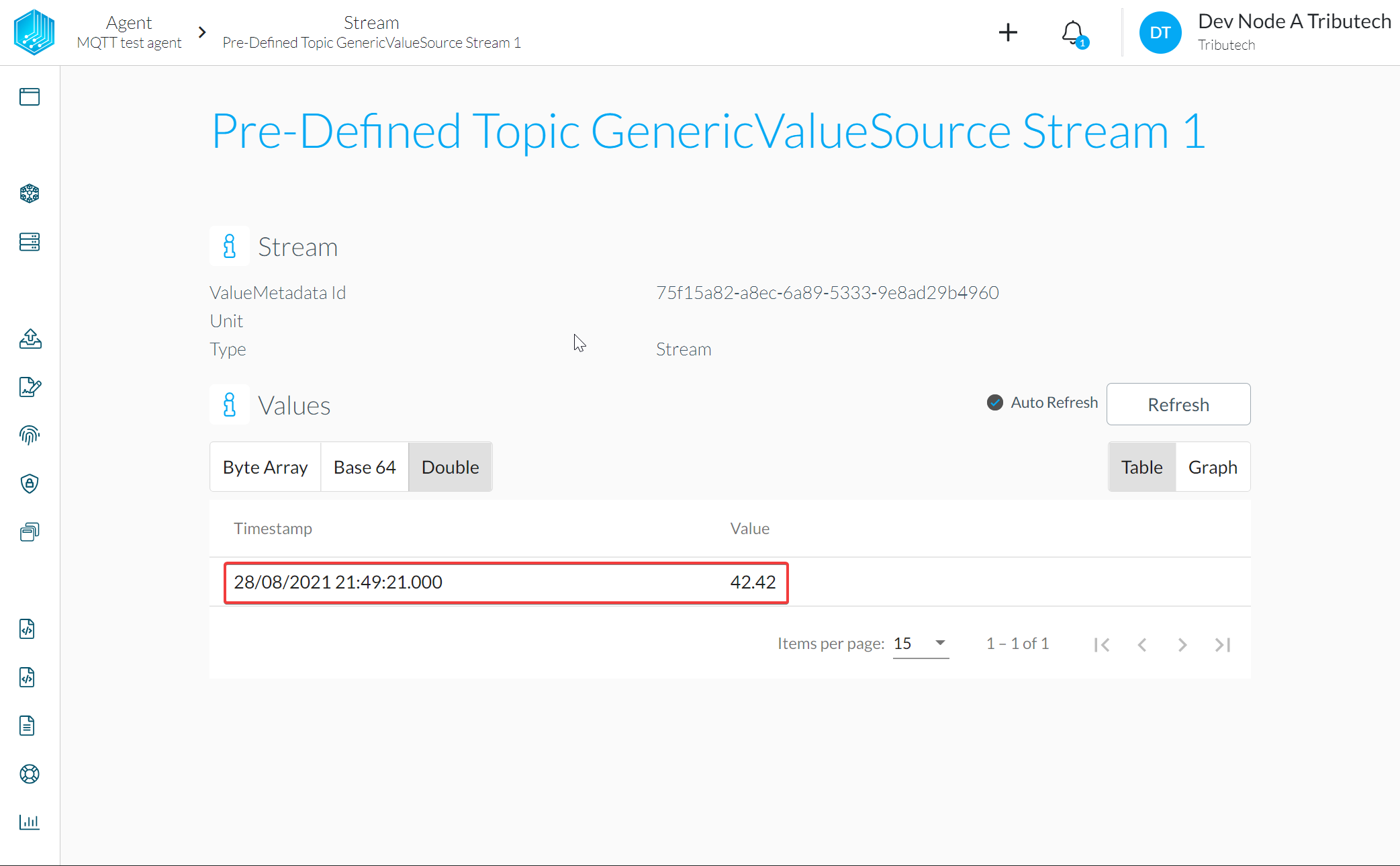
- Verify value for published message in DataSpace-Admin at Streams of Agent
GenericValueSource topic
TOPIC: DSK/EdgeAgent/GenericValueSource
For publishing of various typed values with custom timestamp and ValueMetadataId derived from custom identifiers.
The payload provided for the topic needs to be a UTF8-encoded string which represents a JSON-object as shown in the following example:
{
"ValueSourceID": "Machine1", // ID of the source
"SensorID": "OperatingIndicator", // ID of the sensor
"Timestamp": "2020-01-01T00:00:01+00:00", // Timestamp for the value
"Value": "9ihcj8I1RUA=" // Base64-encoded raw-bytes of the actual value
}
The mapping of MQTT message to the value for the stream works like the following:
ValueMetadataId: Derived automatically in a deterministic manner based onValueSourceIDandSensorIDfrom the JSON-object. Currently there is no check that a matching stream exist we however recommend to create a Generic Stream for each publishedValueSourceIDandSensorIDcombination for easier management.Timestamp:Timestampfrom the JSON-object. (Format ISO 8601-1:2019)Values:Valuefrom the JSON-object as Base64-encoded raw-bytes of the actual value (see Data encoding).
Configure:
- Open the Agent Companion, login to the DSK Node and connect with the DKS Edge Agent
- Add Generic Source

- Add Generic Stream(s) and use
ValueMetadataIdderived fromAgentID,ValueSourceIDandSensorID
Can be derived using the following script https://dotnetfiddle.net/5UeG7C.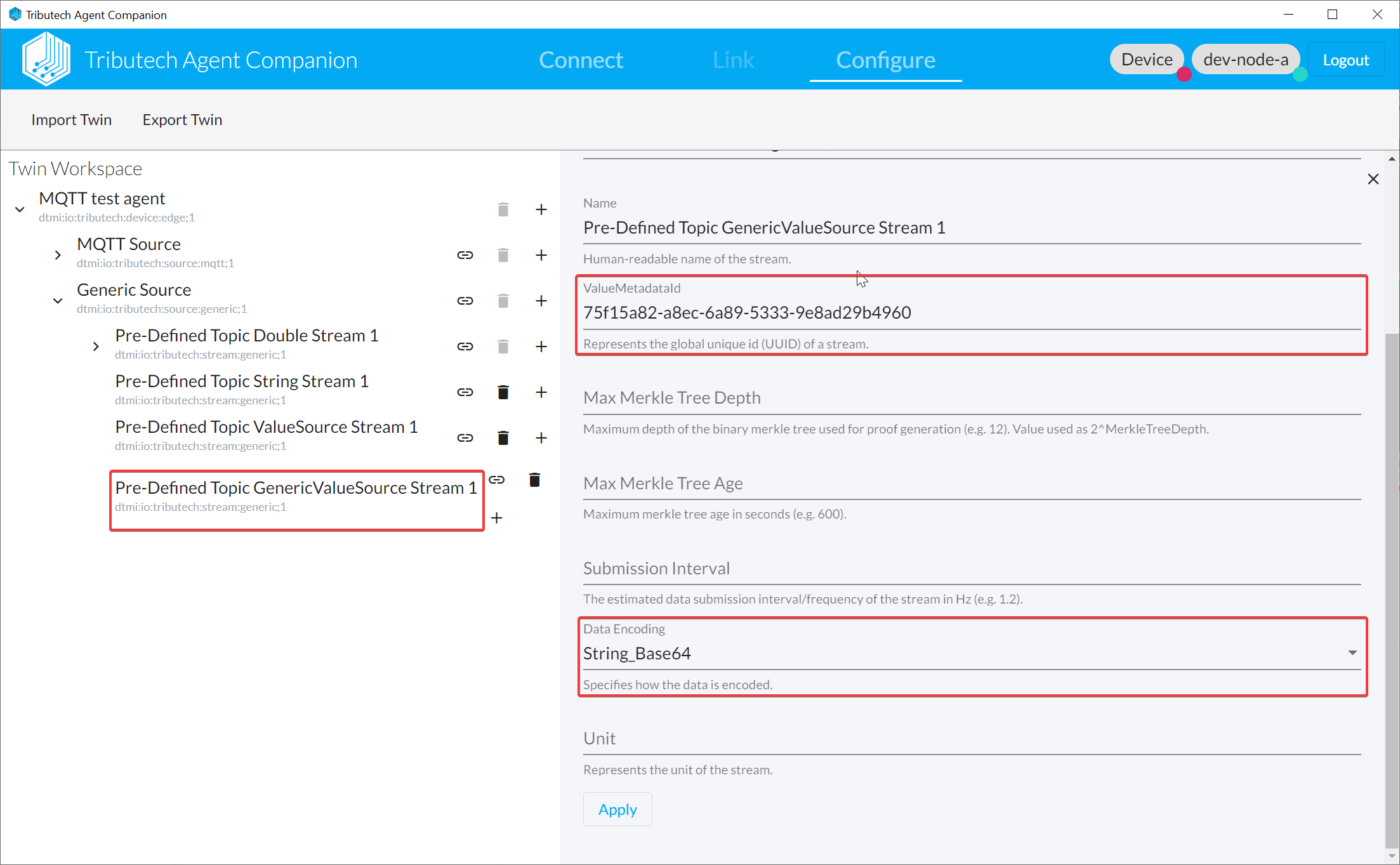
- Upload To Device
Test and verify:
- Publish MQTT message on topic
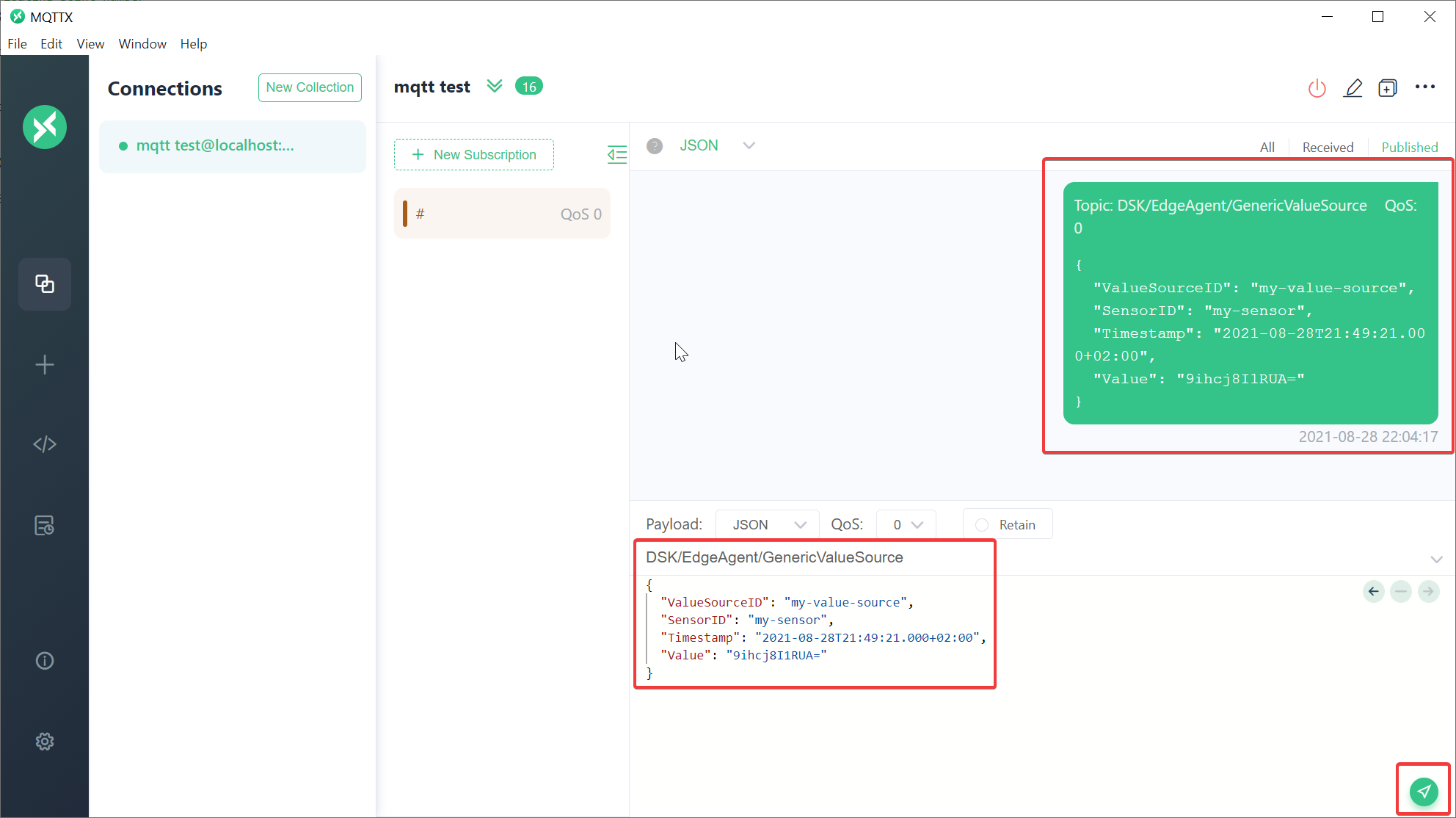
- Verify value for published message in DataSpace-Admin at Streams of Agent
Data encoding
For the data encoding and conversion to other formats we use the industry standards as e.g. implemented by the .NET framework (see e.g. System.BitConverter). The following sample program demonstrates conversions for various value types which might be handy.
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
const string formatter = "{0,-10}{1,10}{2,20}{3,15}{4,40}";
// float
float floatValue = 3.1415926535f;
byte[] floatAsBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(floatValue);
string floatBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(floatAsBytes, 0, floatAsBytes.Length);
string floatHex = BitConverter.ToString(floatAsBytes).Replace("-","");
float floatFromBytes = BitConverter.ToSingle(floatAsBytes);
// double
double doubleValue = 42.42d;
byte[] doubleAsBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(doubleValue);
string doubleBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(doubleAsBytes, 0, doubleAsBytes.Length);
string doubleHex = BitConverter.ToString(doubleAsBytes).Replace("-","");
double doubleFromBytes = BitConverter.ToDouble(doubleAsBytes);
// int (aka int32)
int intValue = 123;
byte[] intAsBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(intValue);
string intBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(intAsBytes, 0, intAsBytes.Length);
string intHex = BitConverter.ToString(intAsBytes).Replace("-","");
int intFromBytes = BitConverter.ToInt32(intAsBytes);
// long (aka int64)
long longValue = 9999;
byte[] longAsBytes = BitConverter.GetBytes(longValue);
string longBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(longAsBytes, 0, longAsBytes.Length);
string longHex = BitConverter.ToString(longAsBytes).Replace("-","");
long longFromBytes = BitConverter.ToInt64(longAsBytes);
// string
string stringValue = "foo";
byte[] stringAsBytes = System.Text.UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(stringValue);
string stringBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(stringAsBytes, 0, stringAsBytes.Length);
string stringHex = BitConverter.ToString(stringAsBytes).Replace("-","");
string stringFromBytes = System.Text.UTF8Encoding.UTF8.GetString(stringAsBytes);
// byte[]
byte[] byteArray = new byte[]{ 0, 100, 120, 210, 255 };
string byteArrayBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(byteArray, 0, byteArray.Length);
string byteArrayHex = BitConverter.ToString(byteArray).Replace("-","");
// print
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "Type", "Value", "HEX", "Base64", "Bytes");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "float", floatValue, floatHex, floatBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", floatAsBytes)}]");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "double", doubleValue, doubleHex, doubleBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", doubleAsBytes)}]");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "int", intValue, intHex, intBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", intAsBytes)}]");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "long", longValue, longHex, longBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", longAsBytes)}]");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "string", stringValue, stringHex, stringBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", stringAsBytes)}]");
Console.WriteLine(formatter, "byte[]", "--", byteArrayHex, byteArrayBase64, $"[{string.Join(", ", byteArray)}]");
}
}
The script can be run online at https://dotnetfiddle.net/5ggm0T.
Output:
Type Value HEX Base64 Bytes
float 3.1415927 DB0F4940 2w9JQA== [219, 15, 73, 64]
double 42.42 F6285C8FC2354540 9ihcj8I1RUA= [246, 40, 92, 143, 194, 53, 69, 64]
int 123 7B000000 ewAAAA== [123, 0, 0, 0]
long 9999 0F27000000000000 DycAAAAAAAA= [15, 39, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
string foo 666F6F Zm9v [102, 111, 111]
byte[] -- 006478D2FF AGR40v8= [0, 100, 120, 210, 255]